 appeler au :
+86 18681515767
appeler au :
+86 18681515767
 email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
 appeler au :
+86 18681515767
appeler au :
+86 18681515767
 email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
01. nos produits
produits chaudsshenzhen jietong technology co., Ltd. est une société de haute technologie spécialisée dans le développement, la production et la vente de systèmes d'identification par radiofréquence (RFID).
toujours un pas de plus!
Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co., Ltd est une entreprise de haute technologie qui se concentre sur la R&D, la production et la vente de matériel RFID UHF. Jietong possède sa propre équipe de R&D dont les ingénieurs ont plus de 10 ans d'expérience en R&D. Afin de fournir le meilleur service et produit au client, Jietong est en développement continu pour offrir une solution complète pour le projet, le service après-vente et le support technologique. Jietong propose des gammes de produits principales, notamment le lecteur de lecture multi-étiquettes UHF RFID Impinj R2000 / TM200 , le lecteur de lecture d'étiquette unique UHF RFID , le lecteur longue portée UHF RFID , le lecteur UHF RFID moyenne portée , le lecteur / enregistreur de bureau UHF RFID , le module de lecteur UHF RFID , lecteur portable UHF RFID , antenne UHF RFID , carte et étiquette UHF RFID , etc., Jietong a le principe de la suprématie des utilisateurs et dépend des nouvelles technologies axées sur le marché et de la haute qualité, nous fournirons les dernières technologies, les meilleurs produits, la compétitivité, le service sincère à nos clients. Nous nous sommes imposés comme une partie fiable, innovante et digne de confiance des entreprises de ses clients et fournisseurs.

02. Pourquoi nous choisir
notre avantagetechnologie co shenzhen jietong. ltd., est une société de haute technologie axée sur la recherche et le développement, la production et la vente de systèmes d'identification par radiofréquence (RFID). professionnel spécial dans le lecteur de la série uhf rfid de l'Internet des objets. jietong a sa propre équipe de recherche et développement dont les ingénieurs ont plus de 10 ans d'expérience en recherche et développement. Afin de fournir le meilleur service et produit au client, jietong est en développement continu pour offrir une solution complète pour le projet, un service après-vente et un support technologique.jietong propose des gammes de produits principales qui incluent le module rfid uhf, le lecteur portable rfid, le lecteur rfid uhf, le lecteur rfid de milieu de gamme pour parking, le lecteur de contrôle d'accès uhf, l'antenne uhf, les cartes et étiquettes uhf, etc.,lecteur jt uhf rfid déjà utilisé de manière intensive dans la gestion des véhicules, l'utilisation de l'environnement comprend également la gestion du personnel pour l'usine, la gestion du poids pour l'entrepôt, le contrôle d'accès pour l'entrepôt et le véhicule, la gestion des vêtements, la gestion de la logistique du tabac, la gestion intelligente de la bibliothèque, la gestion de l'identification de la ligne de production, l'actif gestion etc.,jietong a le principe de la suprématie des utilisateurs, et dépend de la nouvelle technologie orientée marché et de haute qualité, nous fournirons la dernière technologie, les meilleurs produits, le service compétitif et sincère à nos clients.
 professionnel
professionnel
l'équipe r & d a plus de 10 ans d'expérience;
 produit
produit
offrir des produits à faible coût, de qualité moyenne et élevée;
 qualité
qualité
protection nationale par brevet pour les produits de marque propre
 un service
un service
2 ans de garantie et 3 ans de maintenance;
03. cas de projet
SOLUTION&CASCette page de solution aide les clients à résoudre le problème de l'installation et de la gestion des applications à l'aide des produits de Jietong Technology. Les éléments suivants sont inclus : Gestion des véhicules Gestion du système personnel UHF Gestion de la ligne de production Gestion de la logistique La gestion d'actifs Gestion d'entrepôt Les véhicules d'assainissement environnemental gèrent Gestion intelligente des bibliothèques
RFID Technology in the Renewable Energy Sector: Applications and Opportunities 1. Introduction As the global renewable energy industry expands, efficient asset management, supply c...
Lire la suite
gestion des véhiculesAvec le développement thérapeutique de l'économie chinoise, le niveau de vie des gens augmente et la possession totale de la voiture a également commencé à cro...
Lire la suite
système de gestion du personnel uhf rfid>> aperçu du systèmeLe système de gestion du personnel à longue distance est le système de gestion du personnel moderne avec la combinaison ...
Lire la suite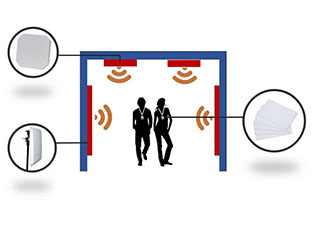
gestion de ligne de productionAfin de produire des produits de meilleure qualité, tout en réduisant les coûts de production et en répondant aux exigences de l'ISO9000, les fabrican...
Lire la suite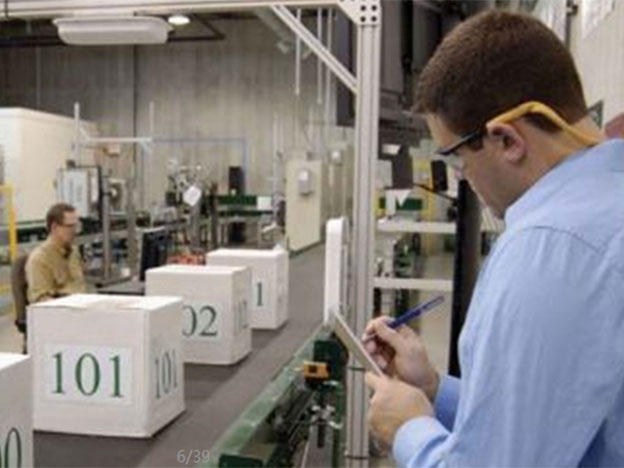
gestion du guidage de voie de chariot agvAvec le niveau de fabrication et la demande croissante des clients, une variété de systèmes logistiques sont confrontés à de nombreux défis...
Lire la suite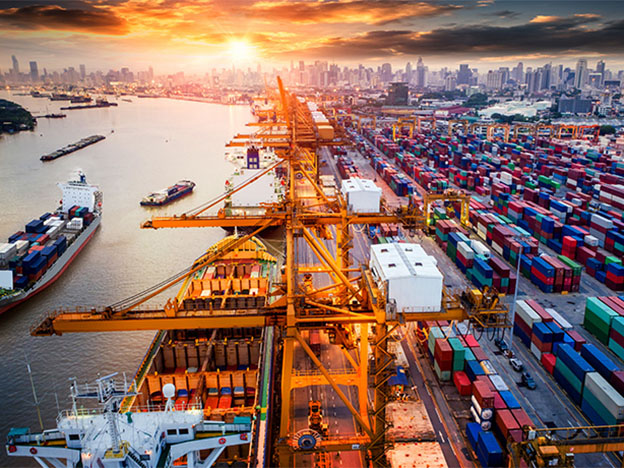
système de gestion des actifs RFIDPrésentation du systèmela manière de mettre en œuvre manuellement la gestion des actifs, y compris l'augmentation des actifs, la distribution, le ...
Lire la suite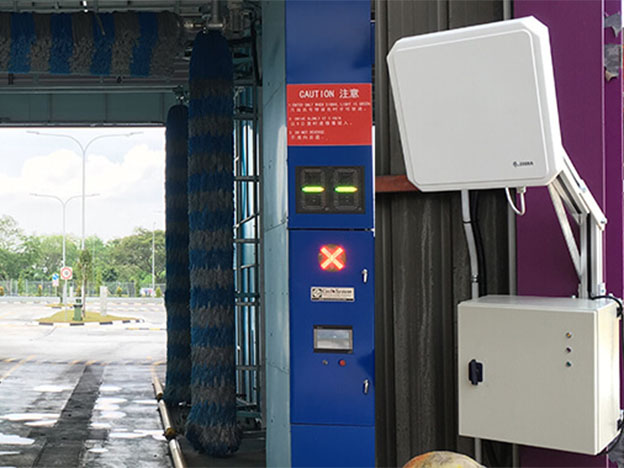
04. événements
dernières nouvellesshenzhen jietong technology co., Ltd. est une société de haute technologie spécialisée dans le développement, la production et la vente de systèmes d'identification par radiofréquence (RFID).


05. consultation gratuite
laisser un messageSi vous êtes intéressé par nos produits et souhaitez en savoir plus, laissez un message ici, nous vous répondrons dès que possible.

téléphone : +86 18681515767
Whatsapp : +8618681515767

email : marketing@jtspeedwork.com

12/F, Building A, No. 6, Shiben Road, Shiyan Street, Bao'an District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China-518108
droits dauteur © 2026 Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co.,Ltd. tous les droits sont réservés.

réseau ipv6 pris en charge